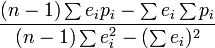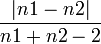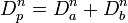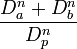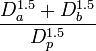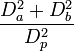|
|
| Line 22: |
Line 22: |
| | | N_stems | | | N_stems |
| | | ''n'' | | | ''n'' |
| − | | | + | | [[File:neuronsomastem.png|150px]] |
| | | Number of stems attached to the soma. | | | Number of stems attached to the soma. |
| | |- | | |- |
| Line 37: |
Line 37: |
| | | N_tips | | | N_tips |
| | | ''n'' | | | ''n'' |
| − | | | + | | [[File:neurontermtip.png|150px]] |
| | | Number of terminal tips of a neuron. | | | Number of terminal tips of a neuron. |
| | |- | | |- |
| Line 257: |
Line 257: |
| | | HillmanThreshold | | | HillmanThreshold |
| | | <math>0.5P + 0.25D1 + 0.25D2</math> | | | <math>0.5P + 0.25D1 + 0.25D2</math> |
| − | P: parent diameter, D1 = 1st daughter diameter, | + | P: parent diameter, \n |
| | + | D1 = 1st daughter diameter, |
| | D2 = 2nd daughter diameter | | D2 = 2nd daughter diameter |
| | | | | | |
L Measures is a research tool for making quantitative morphological measurements from neuronal reconstructions. Features include area measurements of soma, length measurements of processes, angular twists and turns of processes, calculation of the number of terminals and bifurcations, and many more.
| Features
|
Formula or Equation
|
Image
|
Description
|
| Soma_Surface
|
Single soma:  (surface area of sphere) (surface area of sphere)
Multiple soma: 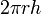 (external area of cylinder) (external area of cylinder)
|
|
Surface area of the soma.
|
| N_stems
|
n
|

|
Number of stems attached to the soma.
|
| N_bifs
|
n
|
|
Number of bifurcations of a neuron.
|
| N_branch
|
n
|
|
Number of branches of a neuron.
|
| N_tips
|
n
|

|
Number of terminal tips of a neuron.
|
| Dimensions
|
|
|
| Width
|
w
|
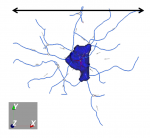
|
Measured along the x-axis of a neuron.
|
| Height
|
h
|
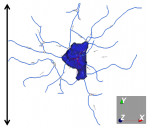
|
Measured along the y-axis of a neuron.
|
| Depth
|
d
|
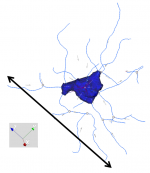
|
Measured along the z-axis of a neuron.
|
| Compartment features
|
|
|
| Type
|
t = 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4
|
|
Compartments are assigned four different types: 1=soma, 2=axon, 3=dendrites, and 4=apical dendrites (are dendrites that emerge from the apex of a pyramidal cell).
|
| Diameter
|
D
|
|
Diameter of each compartment of the neuron.
|
| Diameter_pow
|
D1.5
|
|
Diameter of each compartment of the neuron raised to the power of 1.5.
|
| Length
|
l
|
|
Measured length of the compartments.
|
| EucDistance
|
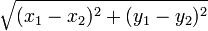
Straight line distance
|
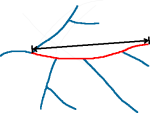
|
Straight line distance between two endpoints of a trace.
|
| PathDistance
|
A + B + C + D + E + ...
|
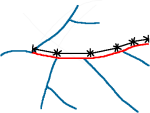
|
Summation of the individual compartment distances that form a trace.
|
| Surface
|
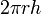
(area of cylinder w/o top and bottom)
|
|
Surface area of the compartments
|
| Section Area
|
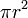
|
|
Cross-sectional area of each compartment.
|
| Volume
|
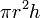
|
|
Volume of the compartments.
|
| Taper_1: Burke Taper
|
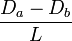
|
|
The change in diameter over pathlength between two critical points (the current and previous one).
|
| Taper_2: Hillman Taper
|
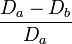
|
|
The ratio of the change in diameter to the initial diameter of two critical points. The initial diameter is usually larger.
|
| Branch features
|
|
|
| Branch_Order
|
n = 0,1,2,3...
|
|
Order of branch with respect to the soma starting at 0 for branches attached to soma.
|
| Branch_pathlength
|
AB + BC + CD + DE + ...
|
|
Summation of the lengths of all the compartments comprising a branch.
|
| Contraction
|
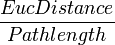
|
|
Ratio between the Euclidean distance of a branch and its path length.
|
| Fragmentation
|
n
|
|
Total number of compartments that form a branch between two bifurcation points, or between a bifurcation point and a terminal tip.
|
| Helix
|
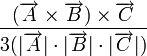
|
|
Helicity of the branches of the neuronal tree. Needs to be at least 3 compartments long to compute the helicity.
|
| Fractal_Dim
|
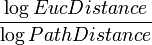 or or
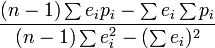
|
|
Fractal dimension metric of the branches in the dendrite trees.
|
| Bifurcation features
|
|
|
| Daughter_Ratio
|
Da / Db
Da = larger daughter diameter
Db = smaller daughter diameter
|
|
Ratio between the diameter of the bigger daughter and the smaller daughter of the current bifurcation. The diameters are measured at the initial part of the branches right when they exit the bifurcation.
|
| Parent_Daughter_Ratio
|
Da / Dp,Db / Dp
|
|
Ratio between the diameter of a daughter and its father for each critical point. The diameters are measured immediately before and after the bifurcation point.
|
| Partition_asymmetry
|
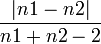
|
|
Compares the symmetry of the processes in terms of the number of tips on the left daughter to the number of tips on the right daughter of a bifurcation.
|
| Rall_Power
|
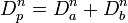
|
|
Best value that fits the equation with extreme 0-5, resolution 1/1000 over the range.
|
| Pk
|
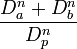
|
|
n = [0, 5]
|
| Pk_classic
|
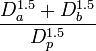
|
|
Rall power is set to 1.5
|
| Pk_2
|
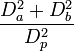
|
|
Rall power is set to 2
|
|
|
|
|
| Bif_ampl_local
|
ϴ (in degrees)
|
|
The local angle formed right at the vertex of the branches; initial angle formed as the two daughter branches exit the bifurcation.
|
| Bif_ampl_remote
|
ϴ
|
|
From the bifurcation, it is the angle to the tips of the two daughter branches. Angle between two branches; angle between the ends of two growing segments (in degrees) at the current bifurcation; angle between the two daughter bifurcations and/or terminal ends (whichever comes first) at the current bifurcation. (Daughter bifurcation means the next bifurcation encountered after the current bifurcation.)
|
| Bif_tilt_local
|
ϴ
|
|
The smaller of the two angles between the end of the parent branch and the initial part of the daughter branches at the bifurcation; angle between the last compartment of the parent branch and the first compartment of each daughter branch at the bifurcation.
- There are two daughter branches for each bifurcation, which gives two angles.
|
| Bif_tilt_remote
|
ϴ
|
|
The smaller of the two angles between the first daughter compartment of the current bifurcating father and the previous father compartment of the previous father bifurcation; angle between the last part of the previous branch and the initial part of the next branches (skipping the branch in-between).
|
| Bif_torque_local
|
ϴ
|
|
Angle between the current plane of bifurcation and the previous plane of bifurcation; the planes are defined by the initial part of the daughter branches as they exit the point of bifurcation.
|
| Bif_torque_remote
|
ϴ
|
|
Angle between the current plane of bifurcation and the previous plane of bifurcation; the plane of bifurcation is defined by a bifurcation and its two daughter bifurcations or terminal ends (whichever comes first).
|
| Terminal bifurcation features
|
|
|
| Terminal_degree
|
n
|
|
Total number of tips of each compartment.
|
| TerminalSegment
|
0 (if not terminal), 1 (if terminal)
|
|
Assigns "1" for all the compartments in the terminal branch.
|
| Last_parent_diam
|
D
|
|
Diameter of last bifurcation before the terminal tips.
|
| Diam_threshold
|
D
|
|
Diameter of first compartment after the terminal bifurcation leading to a terminal tip; initial diameter of the branch exiting the terminal bifurcation.
|
| HillmanThreshold
|
0.5P + 0.25D1 + 0.25D2
P: parent diameter, \n
D1 = 1st daughter diameter,
D2 = 2nd daughter diameter
|
|
Computes the weighted average diameter between 50% of father and 25% of daughter diameters of the terminal bifurcation.
|
| Hausdorff
|
...
|
|
Hausdorff dimension is a fractal dimension using the box counting method. Count the number of boxes required to cover the set.
|
Note: Branches are modeled as a series of compartments. Critical points refer to bifurcation points and terminal tips.
 (surface area of sphere)
(surface area of sphere)
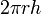 (external area of cylinder)
(external area of cylinder)








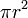
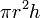
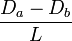
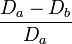
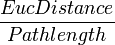
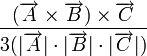
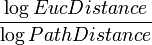 or
or