Equations for 3D Haralick Texture Feature
From FarsightWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Textural Features) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Equations for 3D Haralick Texture features[1], which are based in a gray-level co-occurrence matrix of the image | ||
==Notation== | ==Notation== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
--<math>p_{x+y}(k):</math> <math> p_{x+y}(k) = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1,i+j=k}^{N_g} p(i,j), k=2,3,...,2N_g </math> | --<math>p_{x+y}(k):</math> <math> p_{x+y}(k) = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1,i+j=k}^{N_g} p(i,j), k=2,3,...,2N_g </math> | ||
| + | <math>p_{x+y}(i)</math> is the probability of co-occurrence matrix coordinates summing to x+y | ||
--<math>p_{x-y}(k):</math> <math> p_{x-y}(k) = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1,|i-j|=k}^{N_g} p(i,j), k=0,1,...,N_g-1 </math> | --<math>p_{x-y}(k):</math> <math> p_{x-y}(k) = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1,|i-j|=k}^{N_g} p(i,j), k=0,1,...,N_g-1 </math> | ||
| + | |||
==Textural Features== | ==Textural Features== | ||
* 1) Angular Second Moment:<math>f_1 = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} p(i,j)^2 </math> | * 1) Angular Second Moment:<math>f_1 = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} p(i,j)^2 </math> | ||
* 2) Contrast:<math>f_2 = \sum_{n=0}^{N_g - 1} n^2 {\sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1,|i-j|=n}^{N_g} p(i,j)} </math> | * 2) Contrast:<math>f_2 = \sum_{n=0}^{N_g - 1} n^2 {\sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1,|i-j|=n}^{N_g} p(i,j)} </math> | ||
| − | * 3) Correlation:<math>f_3 = \cfrac{\sum_i \sum_j (i,j)p(i,j)-u_x u_y}{\sigma_x \sigma_y}</math> | + | * 3) Correlation:<math>f_3 = \cfrac{\sum_i \sum_j (i,j)p(i,j)-u_x u_y}{\sigma_x \sigma_y}</math>, where <math>u_x</math>,<math>u_y</math>,<math>\sigma_x</math>,<math>\sigma_y</math> are the means and std.deviations of <math>p_x</math> and <math>p_y</math>, the partial probability density functions |
* 4) Sum of the Squares of Variance: <math>f_4 = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} (i-j)^2 p(i,j)</math> | * 4) Sum of the Squares of Variance: <math>f_4 = \sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} (i-j)^2 p(i,j)</math> | ||
* 5) Inverse Difference Moment: <math>f_5 = \sum_i \sum_j \cfrac{1}{1+(i-j)^2}p(i,j)</math> | * 5) Inverse Difference Moment: <math>f_5 = \sum_i \sum_j \cfrac{1}{1+(i-j)^2}p(i,j)</math> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 28: | ||
* 7) Sum Variance: <math>f_7 = \sum_{i=2}^{2N_g}(i-f_8)^2 p_{x+y}(i)</math> | * 7) Sum Variance: <math>f_7 = \sum_{i=2}^{2N_g}(i-f_8)^2 p_{x+y}(i)</math> | ||
* 8) Sum Entropy: <math>f_8 = - \sum_{i=2}^{2N_g}p_{x+y}(i)log(p_{x+y}(i))</math> | * 8) Sum Entropy: <math>f_8 = - \sum_{i=2}^{2N_g}p_{x+y}(i)log(p_{x+y}(i))</math> | ||
| − | * 9) | + | * 9) Entropy: <math>f_9 = -\sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} p(i,j)log(p(i,j))</math> |
| − | * 10) Difference Variance: <math> | + | * 10) Difference Variance: <math>f_{10} = \sum_{i=0}^{N_g-1} i^2 p_{x-y}(i)</math> |
| − | * 11) Difference Entropy: <math> | + | * 11) Difference Entropy: <math>f_{11}= -\sum_{i=0}^{N_g-1} p_{x-y}(i)log(p_{x-y}(i))</math> |
| − | * | + | * 12) Information Measures of Correlation 1: <math>f_{12} = \cfrac{HXY-HXY1}{max(HX,HY)}</math> |
| + | * 13) Information Measures of Correlation 2: <math>f_{13} = (1-exp(-2.0|HXY2-HXY|))^{1/2}</math>, with <math>HXY = -\sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} p(i,j)log(p(i,j))</math>, | ||
| + | <math>HXY1 = -\sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} p(i,j)log(p_x(i) p_y(i))</math>, | ||
| + | <math>HXY2 = -\sum_{i=1}^{N_g} \sum_{j=1}^{N_g} p_x(i)p_y(j)log(p_x(i) p_y(i))</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information about the Textural features, please refer to [1]. | ||
| + | == Reference == | ||
| + | * [1] R. Haralick, K. Shanmugam, and I. Dinstein, "Textural features for image classification," IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC-3, 610-621, 1973. | ||
Latest revision as of 03:22, 27 April 2009
Equations for 3D Haralick Texture features[1], which are based in a gray-level co-occurrence matrix of the image
Notation
--p(i,j): (i,j)th entry in a normalized gray-tone spatial dependence matrix, p(i,j) = P(i,j) / R * P(i,j) is the co-occurrence matrix and R is the sum of values in it, thus P(i,j) can be considered as the joint distribution of i and j, which are gray levels of the original image. The value of entry p(i,j) is supposed to be very small due to the large size of the co-occurrence matrix.
--px(i) / py(i): ith entry in the marginal-probability distribution matrix obtained by summing the rows/columns of p(i,j).
--Ng: Number of distinct gray levels in the image.
--px + y(k):px + y(i) is the probability of co-occurrence matrix coordinates summing to x+y
--px − y(k):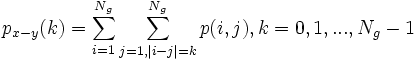
Textural Features
- 1) Angular Second Moment:
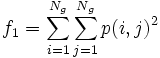
- 2) Contrast:
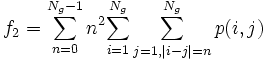
- 3) Correlation:
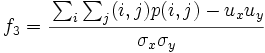 , where ux,uy,σx,σy are the means and std.deviations of px and py, the partial probability density functions
, where ux,uy,σx,σy are the means and std.deviations of px and py, the partial probability density functions
- 4) Sum of the Squares of Variance:
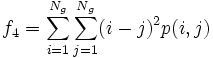
- 5) Inverse Difference Moment:
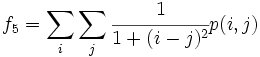
- 6) Sum Average:
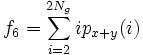
- 7) Sum Variance:
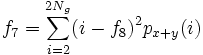
- 8) Sum Entropy:
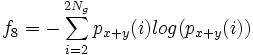
- 9) Entropy:
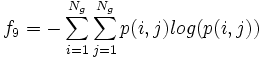
- 10) Difference Variance:
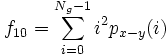
- 11) Difference Entropy:
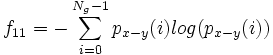
- 12) Information Measures of Correlation 1:
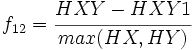
- 13) Information Measures of Correlation 2: f13 = (1 − exp( − 2.0 | HXY2 − HXY | ))1 / 2, with
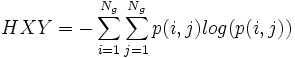 ,
,
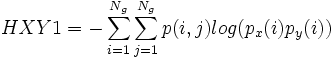 ,
,
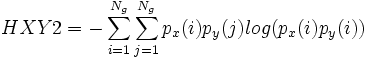
For more information about the Textural features, please refer to [1].
Reference
- [1] R. Haralick, K. Shanmugam, and I. Dinstein, "Textural features for image classification," IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, SMC-3, 610-621, 1973.