MDL Usage
From FarsightWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Code Components) |
m (Program Instruction moved to MDL Usage: more accurate title) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Code Components == | == Code Components == | ||
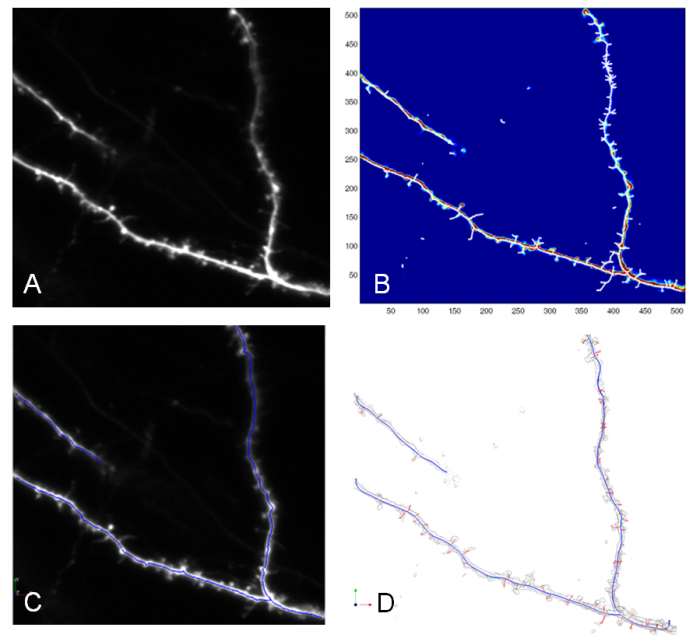
| − | [[Image:Program_result_example.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:Program_result_example.png|thumb|700px|center|Example of program results of skeleton points, backbone extraction and dendritic tree. (A) Original 3D image on 2D z-projection, (B) 3D Skeleton points after path-line formation method, (C) Extracted dendritic backbone, (D) Resultant dendritic tree of MDL backbone and spine models. ]] |
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* ConnComntwFldfill: Connected component analysis algorithm with flood filling method (to prevent from memory outflow problem) | * ConnComntwFldfill: Connected component analysis algorithm with flood filling method (to prevent from memory outflow problem) | ||
<blockquote>''Compute Connected Component with Flood filling method DepthFirstSearch may cause stack overflow for large datasets. <br /> | <blockquote>''Compute Connected Component with Flood filling method DepthFirstSearch may cause stack overflow for large datasets. <br /> | ||
| − | Input and output: 3D image volume | + | Input and output: 3D image volume <br /> |
| + | sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z <br /> | ||
| + | threshold: connected components size | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
Usage: ConnComntwFldfill <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold> | Usage: ConnComntwFldfill <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
<blockquote>''Label the connected components of the input volume with zero background and remove the connected components with small number of voxels. <br /> | <blockquote>''Label the connected components of the input volume with zero background and remove the connected components with small number of voxels. <br /> | ||
Input: original volume <br /> | Input: original volume <br /> | ||
| − | Output: removed small objects''</blockquote> | + | Output: removed small objects <br /> |
| + | sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z <br /> | ||
| + | threshold: not used''</blockquote> | ||
Usage: ConnectComponents <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold> | Usage: ConnectComponents <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold> | ||
* Floodfill: Image floodfill algorithm | * Floodfill: Image floodfill algorithm | ||
<blockquote>''Flood filling accept a sequence of volumes. Input data contains either 0 or values greater or equal to 3.<br /> | <blockquote>''Flood filling accept a sequence of volumes. Input data contains either 0 or values greater or equal to 3.<br /> | ||
| − | Input and output: 3D image volume | + | Input and output: 3D image volume <br /> |
| + | sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ, sizeTime: 3D volume dimension of X, Y, Z and time t<br /> | ||
| + | threshold: not used | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
Usage: Floodfill <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <sizeTime> <output file> <threshold> | Usage: Floodfill <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <sizeTime> <output file> <threshold> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 48: | ||
<blockquote>''Compute the gradient vector field of any 3D intensity map.<br /> | <blockquote>''Compute the gradient vector field of any 3D intensity map.<br /> | ||
Input : 3D volume density map with any sizes <br /> | Input : 3D volume density map with any sizes <br /> | ||
| − | Output: ASCII file with vector 3 components for all object voxels | + | Output: ASCII file with vector 3 components for all object voxels <br /> |
| + | xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z <br /> | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
Usage: GradientVecField <volfile> <xs> <ys> <zs> <outfile> | Usage: GradientVecField <volfile> <xs> <ys> <zs> <outfile> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 56: | ||
<blockquote>''Extract the ridges and valleys feature in 3D vector field <br /> | <blockquote>''Extract the ridges and valleys feature in 3D vector field <br /> | ||
Input: 3D vector field <br /> | Input: 3D vector field <br /> | ||
| − | Output: 3D image-scalar field | + | Output: 3D image-scalar field <br /> |
| + | xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z <br /> | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
Usage: Skel_Extrvalley3D <Input vectors> <xs> <ys> <zs> <Output scalars> | Usage: Skel_Extrvalley3D <Input vectors> <xs> <ys> <zs> <Output scalars> | ||
| Line 57: | Line 65: | ||
Input: 1. 3D vector field <br /> | Input: 1. 3D vector field <br /> | ||
2. Seed points <br /> | 2. Seed points <br /> | ||
| − | Output: | + | Output: skeleton file <br /> |
| + | xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z <br /> | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
Usage: Skel_streamline <vector file> <xs> <ys> <zs> <seeds file> <out skel> | Usage: Skel_streamline <vector file> <xs> <ys> <zs> <seeds file> <out skel> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 72: | ||
* MinSpanTree: MDL algorithm for graph (tree) generation | * MinSpanTree: MDL algorithm for graph (tree) generation | ||
<blockquote>''Generate MDL graph structure from a list of 3D points. <br /> | <blockquote>''Generate MDL graph structure from a list of 3D points. <br /> | ||
| − | Input format: .skel (3D points) <br /> | + | Input format: 1. .skel (3D points) <br /> |
| − | Output format: .swc or .vtk (3D graph format) | + | 2. 3D image volume <br /> |
| + | Output format: .swc or .vtk (3D graph format) <br /> | ||
| + | dir: working directory <br /> | ||
| + | xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z <br /> | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
| − | Usage: MinSpanTree < | + | Usage: MinSpanTree <dir> <skel pt file> <vol file> <xs> <ys> <zs> <out vtk graph> |
* VolumeProcess: Image preprocessing algorithms (including image operations, crop, scale, etc.) | * VolumeProcess: Image preprocessing algorithms (including image operations, crop, scale, etc.) | ||
<blockquote>''Volume dataset processing accepts a sequence of volumes <br /> | <blockquote>''Volume dataset processing accepts a sequence of volumes <br /> | ||
| − | + | Function selection <br /> | |
| − | 1. sizeExpand <br /> | + | 1. choose sizeExpand for different output volume size<br /> |
| − | 2. preproess | + | 2. preproess methods <br /> |
| + | Input and output: 3D image volume <br /> | ||
| + | sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ, sizeTime: 3D volume dimension of X, Y, Z and time t<br /> | ||
| + | threshold: intensity threshold | ||
</blockquote>'' | </blockquote>'' | ||
Usage: VolumeProcess <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <sizeTime> <output file> <threshold> | Usage: VolumeProcess <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <sizeTime> <output file> <threshold> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:20, 3 July 2009
File Formats
filename.raw: 3D volume dataset with dimension indicated by the filename (x*y*z), with no header. filename.seed: text file with high curvature seed points, which contains a list of 3D points. filename.skel: text file with skeleton points, which contains a list of 3D points. filename.swc: file format to describe dendritic morphology. The branches of a dendritic tree are represented as a set of cylinders. filename.vtk: common vtk format, which contains MDL skeleton output.
Code Components
- AnisoDiffuse: Image smoothing algorithm – Anisotropic Diffusion
It is an iterative method that can produce smooth results while keeping useful edge structures.
Input and output: 3D image volume
sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
threshold: not used
Usage: AnisoDiffuse <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold>
- ConnComntwFldfill: Connected component analysis algorithm with flood filling method (to prevent from memory outflow problem)
Compute Connected Component with Flood filling method DepthFirstSearch may cause stack overflow for large datasets.
Input and output: 3D image volume
sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
threshold: connected components size
Usage: ConnComntwFldfill <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold>
- ConnectComponents: Connected component analysis algorithm with scanline filling method
Label the connected components of the input volume with zero background and remove the connected components with small number of voxels.
Input: original volume
Output: removed small objects
sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
threshold: not used
Usage: ConnectComponents <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <output file> <threshold>
- Floodfill: Image floodfill algorithm
Flood filling accept a sequence of volumes. Input data contains either 0 or values greater or equal to 3.
Input and output: 3D image volume
sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ, sizeTime: 3D volume dimension of X, Y, Z and time t
threshold: not used
Usage: Floodfill <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <sizeTime> <output file> <threshold>
- GradientVecField: Computing gradient vector field from intensity images
Compute the gradient vector field of any 3D intensity map.
Input : 3D volume density map with any sizes
Output: ASCII file with vector 3 components for all object voxels
xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
Usage: GradientVecField <volfile> <xs> <ys> <zs> <outfile>
- Skel_Extrvalley3D: Computing high curvature seed points
Extract the ridges and valleys feature in 3D vector field
Input: 3D vector field
Output: 3D image-scalar field
xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
Usage: Skel_Extrvalley3D <Input vectors> <xs> <ys> <zs> <Output scalars>
- Skel_streamline: Producing 3D skeleton points from vector field and seed points
Form path-lines from saddle points and seed points
Input: 1. 3D vector field
2. Seed points
Output: skeleton file
xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
Usage: Skel_streamline <vector file> <xs> <ys> <zs> <seeds file> <out skel>
- MinSpanTree: MDL algorithm for graph (tree) generation
Generate MDL graph structure from a list of 3D points.
Input format: 1. .skel (3D points)
2. 3D image volume
Output format: .swc or .vtk (3D graph format)
dir: working directory
xs, ys, zs: 3D volume dimension of X, Y and Z
Usage: MinSpanTree <dir> <skel pt file> <vol file> <xs> <ys> <zs> <out vtk graph>
- VolumeProcess: Image preprocessing algorithms (including image operations, crop, scale, etc.)
Volume dataset processing accepts a sequence of volumes
Function selection
1. choose sizeExpand for different output volume size
2. preproess methods
Input and output: 3D image volume
sizeX, sizeY, sizeZ, sizeTime: 3D volume dimension of X, Y, Z and time t
threshold: intensity threshold
Usage: VolumeProcess <input file> <sizeX> <sizeY> <sizeZ> <sizeTime> <output file> <threshold>
Python Wrapping
This python code gives an example of program run on dataset MBFsp5 with dimension x-308, y-512 and z-49.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import os
data_dir = "/projects/MDLCode/zackdata"
os.system("volumeProcess/volumeProcess %s/MBFsp5.308x512x49.raw 308 512 49 1 %s/volume_Processed.raw 2" % (data_dir, data_dir))
os.system("ConnCompntwFldfill/ConnCompntwFldfill %s/volume_Processed.raw 308 512 49 %s/components_Connected.raw 100" % (data_dir, data_dir))
os.system("AnisoDiffuse/AnisoDiffuse %s/components_Connected.raw 308 512 49 %s/Aniso_Diffused.raw 0" % (data_dir, data_dir))
os.system("GradientVecField/GradientVecField %s/Aniso_Diffused.raw 308 512 49 %s/out.vec" % (data_dir, data_dir))
os.system("skel_Extrvalley3D/skel_Extrvalley3D %s/out.vec 308 512 49 %s/out.seed" % (data_dir, data_dir))
os.system("skel_streamline/skel_streamline %s/out.vec 308 512 49 %s/out.seed %s/out.skel" % (data_dir, data_dir, data_dir))
os.system("MinSpanTree/MinSpanTree %s/ out.skel components_Connected.raw 308 512 49 %s/out.vtk out.txt %s/Aniso_Diffused.raw" % (data_dir, data_dir, data_dir))