Intrinsic Features of Blobs
From FarsightWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Features) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
These features can be calculated with two input images (Data Image and Label Image). | These features can be calculated with two input images (Data Image and Label Image). | ||
They are most commonly used for blob-like regions, such as cell nuclei. | They are most commonly used for blob-like regions, such as cell nuclei. | ||
| + | Equations are shown for 3-dimensional space unless otherwise noted. | ||
| − | {| border="1px" cellpadding=" | + | == Glossary of Notation == |
| + | {| border="1px" cellpadding="3" style="text-align:left" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Name | + | | <math>p=(x,y,z)</math> |
| − | | Description | + | | the coordinate of a voxel (three-dimensional point in a volume image) |
| − | | Formula | + | |- |
| + | | <math>N_p</math> | ||
| + | | a neighbor voxel of <math>p</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>l_p</math> | ||
| + | | the segmentation label at <math>p</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>I_i(p)</math> | ||
| + | | the intensity value of <math>p</math> at <math>i^{th}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>\Omega = \{p|l_p = o\}</math> | ||
| + | | the set of voxels of an object <math>o</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>\Omega_s = \{l_p = o; \exists N_p, l_{N_p} \neq o\}</math> | ||
| + | | the set of surface voxels of the object | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>\Omega_{in} = \Omega - \Omega_s</math> | ||
| + | | the set of interior voxels of an object | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>\overline{p}</math> | ||
| + | | the center of mass of the object | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>P(I)</math> | ||
| + | | Probability Density Function (PDF) of intensity values <math>I</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>M_{p,q,r} = \sum_{z=0}^{Z-1}\sum_{y=0}^{Y-1}\sum_{x=0}^{X-1}x^p y^q z^r I(x,y,z)</math> | ||
| + | | Raw Moment of discrete image <math>I</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>\lambda_i</math> | ||
| + | | <math>i^{th}</math> eigenvalue of covariance matrix | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <math>\overline{v_i}</math> | ||
| + | | eigenvector corresponding to <math>\lambda_i</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Features == | ||
| + | {| border="1px" cellpadding="3" style="text-align:left" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Name''' | ||
| + | | '''Units''' | ||
| + | | '''Description''' | ||
| + | | '''Formula''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Volume | | Volume | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| Number of voxels in the object [1] | | Number of voxels in the object [1] | ||
| − | | <math>|\Omega|</math> | + | | <math>|\Omega|</math> or <math>M_{000}|\{I=binary\}</math> |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Integrated Intensity | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Sum of the intensities of all voxels in the object [1] | ||
| + | | <math>\sum I(\Omega)</math> or <math>M_{000}|\{I=intensity\}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Centroid | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | Center of the object [1] | ||
| + | | <math> \left [ \begin{array}{ccc} \frac{M_{100}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{010}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{001}}{M_{000}} \end{array} \right ]|\{I=binary\} </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Weighted Centroid | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | Uses the image intensity values to calculate the center of mass of the object [1] | ||
| + | | <math> \left [ \begin{array}{ccc} \frac{M_{100}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{010}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{001}}{M_{000}} \end{array} \right ]|\{I=intensity\} </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Axes Lengths | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | The length of the axes of the ND hyper-ellipsoid fit to the object [1] | ||
| + | | <math>4\sqrt{\lambda_i}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Eccentricity | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ratio of the distance between the foci of the best-fit hyper-ellipsoid to the length of its major axis. (2D) [1] | ||
| + | | <math>\sqrt{\frac{\lambda_1 - \lambda_0}{\lambda_1}}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elongation | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ratio of the major axis length to minor axis length of the best-fit hyper-ellipsoid. (2D) [1] | ||
| + | | <math>\frac{\lambda_1}{\lambda_0}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Orientation | ||
| + | | radians | ||
| + | | Angle between the major axis of the best-fit hyper-ellipsoid and origin. (2D) [1] | ||
| + | | <math>tan^{-1}\left(\frac{\overline{v_1}(1)}{\overline{v_1}(0)}\right)</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Bounding Box Volume | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | Number of voxels in the bounding box of the object [1] | ||
| + | | (max(X)-min(X)+1) * (max(Y)-min(Y)+1) * ... | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Oriented Bounding Box Volume | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | Number of voxels in the oriented bounding box of the object. The oriented bounding box is defined as the bounding box aligned along the axes of the object. [1] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Sum | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Same as integrated intensity [2] | ||
| + | | <math>\sum I(\Omega)</math> or <math>M_{000}|\{I=intensity\}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mean | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Average intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| + | | <math>\frac{1}{|\Omega|}\sum I(\Omega)</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Median | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Middle intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Minimum | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Minimum intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Maximum | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Maximum intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Sigma | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Standard deviation of intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| + | | <math>\sigma_I</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Variance | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Variance of intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| + | | <math>\sigma_I^2</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Radius Variation | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | Standard deviation of distance from surface voxels to centroid | ||
| + | | stddev<math>(\|\Omega_s - \overline{p}\|)</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Skew | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Skew of the PDF [3] | ||
| + | | <math>\frac{1}{\sigma_I^3}\sum_{I=0}^{255}(I-\overline{I})^3P(I)</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Energy | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Energy of the PDF[3] | ||
| + | | <math>\sum_{I=0}^{255}[P(I)]^2</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Entropy | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Entropy of the PDF [3] | ||
| + | | <math>-\sum_{I=0}^{255}P(I)\log_2{P(I)}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Surface Gradient | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Average of surface gradients | ||
| + | | <math>mean(G(\Omega_s))</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Interior Gradient | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Average of interior gradients | ||
| + | | <math>mean(G(\Omega_{in}))</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Interior Intensity | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Average of interior intensities | ||
| + | | <math>mean(I(\Omega_{in}))</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Surface Intensity | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Average of surface intensities | ||
| + | | <math>mean(I(\Omega_s))</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Intensity Ratio | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ratio of surface intensity to interior intensity | ||
| + | | <math>\frac{mean(I(\Omega_s))}{mean(I(\Omega_{in}))}</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shared Boundary | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ratio of object "edges" that touch another object to total number of object "edges | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Surface Area | ||
| + | | voxels | ||
| + | | Number of voxels on surface of the object [4] | ||
| + | | <math>|\Omega_s|</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shape | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Ratio of surface voxels to total voxels - compactness or thinness of object [5] | ||
| + | | <math>\frac{|\Omega_s|^3}{36\pi|\Omega|^2}</math> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | == References == |
| − | + | [1] [http://www.insight-journal.org/browse/publication/301 itkLabelGeometryImageFilter]<br> | |
| − | < | + | [2] [http://www.itk.org/Doxygen312/html/classitk_1_1LabelStatisticsImageFilter.html itkLabelStatisticsImageFilter]<br> |
| − | + | [3] Umbaugh, S. E., Y.-S. Wei, et al. (1997). "Feature extraction in image analysis. A program for facilitating data reduction in medical image classification." Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE 16(4): 62-73.<br> | |
| − | + | [4] Lohmann, G. (1998). Volumetric Image Analysis, Wiley <br> | |
| − | + | [5] Theodoridis, S. and K. Koutroumbas (1999). Pattern recognition. San Diego, Academic Press. <br> | |
| − | + | [6] [http://kitware.com/products/archive/kitware_quarterly0109.pdf Kitware Source Newsletter] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | [http://kitware.com/products/archive/kitware_quarterly0109.pdf Kitware Source Newsletter] | + | |
Latest revision as of 18:39, 27 May 2009
These features can be calculated with two input images (Data Image and Label Image). They are most commonly used for blob-like regions, such as cell nuclei. Equations are shown for 3-dimensional space unless otherwise noted.
Glossary of Notation
| p = (x,y,z) | the coordinate of a voxel (three-dimensional point in a volume image) |
| Np | a neighbor voxel of p |
| lp | the segmentation label at p |
| Ii(p) | the intensity value of p at ith |
| Ω = {p | lp = o} | the set of voxels of an object o |
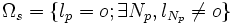
|
the set of surface voxels of the object |
| Ωin = Ω − Ωs | the set of interior voxels of an object |
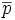
|
the center of mass of the object |
| P(I) | Probability Density Function (PDF) of intensity values I |
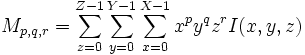
|
Raw Moment of discrete image I |
| λi | ith eigenvalue of covariance matrix |
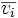
|
eigenvector corresponding to λi |
Features
| Name | Units | Description | Formula |
| Volume | voxels | Number of voxels in the object [1] | | Ω | or M000 | {I = binary} |
| Integrated Intensity | Sum of the intensities of all voxels in the object [1] | 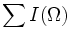 or M000 | {I = intensity} or M000 | {I = intensity}
| |
| Centroid | voxels | Center of the object [1] | ![\left [ \begin{array}{ccc} \frac{M_{100}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{010}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{001}}{M_{000}} \end{array} \right ]|\{I=binary\}](/mw/images/math/c/0/4/c04ebc21359578e839e7056b6f67a774.png)
|
| Weighted Centroid | voxels | Uses the image intensity values to calculate the center of mass of the object [1] | ![\left [ \begin{array}{ccc} \frac{M_{100}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{010}}{M_{000}}, & \frac{M_{001}}{M_{000}} \end{array} \right ]|\{I=intensity\}](/mw/images/math/0/5/c/05c7b86bceb7a3bb6f5b4d3f3fe529ef.png)
|
| Axes Lengths | voxels | The length of the axes of the ND hyper-ellipsoid fit to the object [1] | 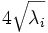
|
| Eccentricity | Ratio of the distance between the foci of the best-fit hyper-ellipsoid to the length of its major axis. (2D) [1] | 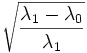
| |
| Elongation | Ratio of the major axis length to minor axis length of the best-fit hyper-ellipsoid. (2D) [1] | 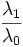
| |
| Orientation | radians | Angle between the major axis of the best-fit hyper-ellipsoid and origin. (2D) [1] | 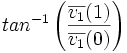
|
| Bounding Box Volume | voxels | Number of voxels in the bounding box of the object [1] | (max(X)-min(X)+1) * (max(Y)-min(Y)+1) * ... |
| Oriented Bounding Box Volume | voxels | Number of voxels in the oriented bounding box of the object. The oriented bounding box is defined as the bounding box aligned along the axes of the object. [1] | |
| Sum | Same as integrated intensity [2] | 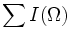 or M000 | {I = intensity} or M000 | {I = intensity}
| |
| Mean | Average intensity of voxels in the object [2] | 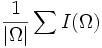
| |
| Median | Middle intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| Minimum | Minimum intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| Maximum | Maximum intensity of voxels in the object [2] | ||
| Sigma | Standard deviation of intensity of voxels in the object [2] | σI | |
| Variance | Variance of intensity of voxels in the object [2] | 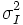
| |
| Radius Variation | voxels | Standard deviation of distance from surface voxels to centroid | stddev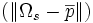
|
| Skew | Skew of the PDF [3] | 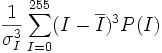
| |
| Energy | Energy of the PDF[3] | ![\sum_{I=0}^{255}[P(I)]^2](/mw/images/math/1/f/d/1fd6f9ae5d3391efdd4dcdc207610330.png)
| |
| Entropy | Entropy of the PDF [3] | 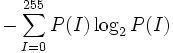
| |
| Surface Gradient | Average of surface gradients | mean(G(Ωs)) | |
| Interior Gradient | Average of interior gradients | mean(G(Ωin)) | |
| Interior Intensity | Average of interior intensities | mean(I(Ωin)) | |
| Surface Intensity | Average of surface intensities | mean(I(Ωs)) | |
| Intensity Ratio | Ratio of surface intensity to interior intensity | 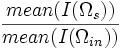
| |
| Shared Boundary | Ratio of object "edges" that touch another object to total number of object "edges | ||
| Surface Area | voxels | Number of voxels on surface of the object [4] | | Ωs | |
| Shape | Ratio of surface voxels to total voxels - compactness or thinness of object [5] | 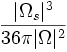
|
References
[1] itkLabelGeometryImageFilter
[2] itkLabelStatisticsImageFilter
[3] Umbaugh, S. E., Y.-S. Wei, et al. (1997). "Feature extraction in image analysis. A program for facilitating data reduction in medical image classification." Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE 16(4): 62-73.
[4] Lohmann, G. (1998). Volumetric Image Analysis, Wiley
[5] Theodoridis, S. and K. Koutroumbas (1999). Pattern recognition. San Diego, Academic Press.
[6] Kitware Source Newsletter